Implementing DevSecOps CI/CD pipelines with RHACS and OpenShift
How you can add Security to your DevOps pipelines? How you can shift left, securing your software lifecycle application development using DevSecOps tools and methods? How we can integrate RHACS in our DevOps pipelines?
Let’s dig in!
Overview
With the advent of DevSecOps, security is put front and center - it is addressed in terms of people, processes, and technology. Security tools are integrated right into the build process and we could easily break the build if security requirements are not met with the security gates that we build into the CI/CD pipeline.
The benefits of DevOps and Continuous Integration / Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) have been demonstrated with great success over the years. Organizations have always sought to do more with less. Security was treated as an add-on to the end of the software delivery process in many cases, and it often delayed software delivery. The industry recognized that this had to change.
The industry recognized that this had to change. Organizations must continue to meet contractual and regulatory obligations as well as internal security standards, but need to accelerate software delivery to capitalize on opportunities. To enable organizations to meet these standards and deliver at the speed of DevOps security has faced the choice of becoming irrelevant or molding to modern software delivery practices.
Security is critical to deliver software quickly and has become a metric of software quality, so there was a push to include “Sec” in “DevOps.”
With the advent of DevSecOps, Shift Left is a practice intended to find and prevent defects early in the software delivery process. Security tools are integrated directly into the build process. As a result, the CI/CD process can move faster and reduce the length of time to delivery while still continuously improving the quality of each release.
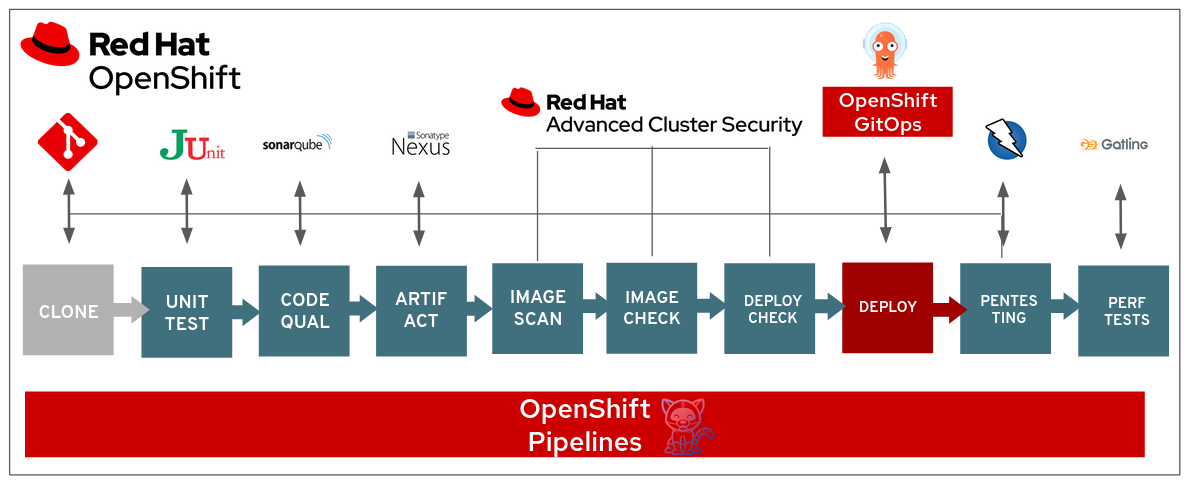
DevSecOps Pipeline - High Level Diagram
This DevSecOps CI/CD pipeline demo will focus on some of the technologies used to implement automated security compliance controls within a typical CI/CD application pipeline.
This DevSecOps demo is available in GitHub and it’s automated in order to deploy and test in any OpenShift environment.
A number of tools will be used and pre-configured to support the DevSecOps pipeline. Most of these tools are running containerized within the Red Hat OpenShift cluster (but can run in other Kubernetes clusters as well).
In our DevSecOps CI/CD pipeline, we will be using several technologies such as:
- OpenShift Pipelines based on Tekton
- OpenShift GitOps based on ArgoCD
- Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes
- OpenShift Container Registry
- SonarQube
- Nexus
- JUnit
- Gogs
- Git Webhook
- Gatling
- Zap Proxy
Application Security Testing Methods in DevSecOps demo
A number of technologies are available to help developers catch security flaws before they’re baked into a final software release. These application security testing methodologies are used to find security vulnerabilities that can make an application susceptible to attack.
These application security testing methodologies that are included in this demo are the following:
-
Static application security testing (SAST), or white box method of testing, which analyzes code under development for vulnerabilities and quality issues.
-
Dynamic application security testing (DAST), is a black box testing method, which examines an application as it’s running to find vulnerabilities that an attacker could exploit.
-
Software composition analysis (SCA), which examines dependent packages included with applications, looking for known vulnerabilities and licensing issues.
-
Interactive application security testing (IAST) and dynamic application security testing (DAST) tools, which analyze running applications to find execution vulnerabilities.
-
Configuration management with analysis and management of application and infrastructure configurations in DevOps. Traditionally this was not used as a way to improve security. But properly managing configurations in a GitOps process can strengthen security by improving change controls, identifying configuration defects that can reduce the attack surface, and signing and tracking authorship for better accountability and opportunities to improve.
-
Image risk is any risk associated with a container image. This includes vulnerable dependencies, embedded secrets, bad configurations, malware, or images that are not trusted.
-
Run-Time Application Security Protection (RASP) which protect the app even if a network’s perimeter defenses are breached and the apps contain security vulnerabilities missed by the development team
Installing the prerequisites for running the DevSecOps demo
For install the DevSecOps demo there are some prerequisites that we need to install before start:
ansible-galaxy collection install community.kubernetes
pip3 install kubernetes
- Install some extra Python dependency:
pip3 install jmespath
Install the DevSecOps demo
This DevSecOps pipeline demo can be installed in any OpenShift 4.7+ cluster using a fully automated deployment and integration of every resource and tool needed.
This automated deployment is based in Ansible, so we can deploy it in a couple of minutes with just a command!
./install.sh
Accessing to the credentials and resources for the DevSecOps demo
Check the resources deployed for this demo with:
./status.sh
- Gogs git server (username/password: gogs/gogs)
- Sonatype Nexus (username/password: admin/admin123)
- SonarQube (username/password: admin/admin)
- Argo CD (username/password: admin/[Login with OAuth using Dex])
- ACS (username/password: admin/StackRox)
- Repository Server (username/password: reports/reports)
Running the DevSecOps Demo
Finally when we have every prerequisite and the bootstrap properly installed in place, we can start and run the demo.
./demo.sh start
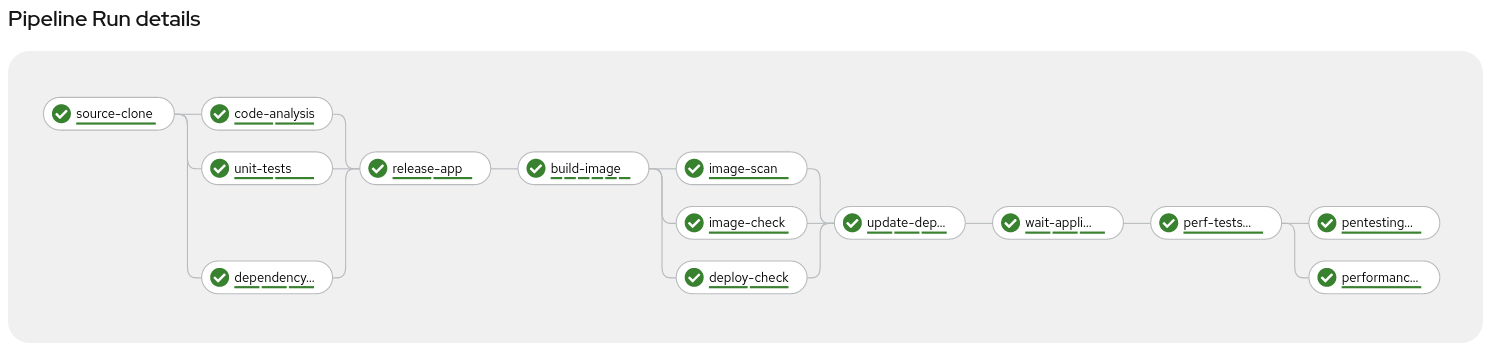
After a while, we can check that the full pipeline was executed properly, and every step was successfully completed:
NOTE: This pipeline will fail if you don’t disable the “Fixable at least Important policy enforcement behaviour of ACS. This is expected to demonstrate the failure when a violation of the system policy occurs.
You can also check this video of the DevSecOps full pipeline demo, with the end2end lifecycle.
In next blog posts, we will deep dive to each step of the DevSecOps CI/CD demo pipeline, making an analysis of the tools, methods and techniques used in the pipelines, and how we can leverage and increase our security in the DevOps pipelines!
NOTE: Opinions expressed in this blog are my own and do not necessarily reflect that of the company I work for.
Happy Shift Lefting!