Generate and Manage ApplicationSets of OpenShift-GitOps/ArgoCD in ACM
How I can connect my ArgoCD/OpenShift GitOps deployments in each managed cluster, and have full visibility, control and management of my Argo Applications in single pane of glass? How I can manage all my ApplicationSets in the different managed clusters that I have across public and private clouds?
Let’s dig in!
Overview
From ACM version 2.3 you can manage ApplicationSets from ArgoCD / OpenShift-GitOps, having a single pane of glass to manage all of your GitOps Applications in a scalable way.
The ApplicationSet controller is a Kubernetes controller that adds support for an ApplicationSet CustomResourceDefinition (CRD).
The ApplicationSet controller, when installed with Argo CD, supplements it by adding additional features in support of cluster-administrator-focused scenarios. The ApplicationSet controller provides:
-
The ability to use a single Kubernetes manifest to deploy multiple applications from one or multiple Git repositories with Argo CD
-
Improved support for monorepos: in the context of Argo CD, a monorepo is multiple Argo CD Application resources defined within a single Git repository
among others features that are interesting for multitenant clustering.
And how we can connect the ACM with the ApplicationSets of OpenShift GitOps for configure and deploy OpenShift GitOps applications and applicationsets in Managed clusters?
Prerequisites for integrate OpenShift GitOps and ACM with Managed Clusters
- We need to install OpenShift GitOps in the ACM Hub with the Operator:
until oc apply -k https://github.com/RedHat-EMEA-SSA-Team/ns-gitops/tree/bootstrap/bootstrap ; do sleep 2; done
-
You can also follow the official documentation for OpenShift GitOps
-
On the other we need to deploy and manage different clusters in public or private cloud. In my case I used my BM cluster located in Munich, Germany and also the cluster deployed in AWS in us-west-1 located in North California, and will be used in this blog post for deploy my applications.
Configuring Managed Clusters for OpenShift GitOps / ArgoCD
To configure and link OpenShift GitOps in ACM, we can register a set of one or more managed clusters to an instance of Argo CD or OpenShift GitOps operator.
After registering, we can deploy applications to those clusters using Application and ApplicationSets managing from the ACM Hub Applications. Then, we can set up a continuous GitOps environment to automate application consistency across clusters in development, staging, and production environments.
- First, we need to create managed cluster sets and add managed clusters to those managed cluster sets:
cat acmgitops/managedclusterset.yaml
apiVersion: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/v1alpha1
kind: ManagedClusterSet
metadata:
name: all-openshift-clusters
spec: {}
- Add the managed clusters as imported clusters into the ClusterSet. You can imported with the ACM Console or with the CLI:
Add Imported clusterset with Console
Add Imported clusterset with CLI
- Create managed cluster set binding to the namespace where Argo CD or OpenShift GitOps is deployed.
cat managedclustersetbinding.yaml
apiVersion: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/v1alpha1
kind: ManagedClusterSetBinding
metadata:
name: all-openshift-clusters
namespace: openshift-gitops
spec:
clusterSet: all-openshift-clusters
oc apply -f managedclustersetbinding.yaml
- In the namespace that is used in managed cluster set binding, create a placement custom resource to select a set of managed clusters to register to an ArgoCD or OpenShift GitOps operator instance:
apiVersion: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/v1alpha1
kind: Placement
metadata:
name: all-openshift-clusters
namespace: openshift-gitops
spec:
predicates:
- requiredClusterSelector:
labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: vendor
operator: "In"
values:
- OpenShift
NOTE: Only OpenShift clusters are registered to an Argo CD or OpenShift GitOps operator instance, not other Kubernetes clusters.
- Create a GitOpsCluster custom resource to register the set of managed clusters from the placement decision to the specified instance of Argo CD or OpenShift GitOps:
apiVersion: apps.open-cluster-management.io/v1alpha1
kind: GitOpsCluster
metadata:
name: argo-acm-clusters
namespace: openshift-gitops
spec:
argoServer:
cluster: local-cluster
argoNamespace: openshift-gitops
placementRef:
kind: Placement
apiVersion: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/v1alpha1
name: all-openshift-clusters
namespace: openshift-gitops
This enables the Argo CD instance to deploy applications to any of those ACM Hub managed clusters.
As we can see from the previous example the placementRef.name is defined as all-openshift-clusters, and is specified as target clusters for the GitOps instance that is installed in argoNamespace: openshift-gitops.
On the other hand, the argoServer.cluster specification requires the local-cluster value, because will be using the OpenShift GitOps deployed in the OpenShift cluster that is also where the ACM Hub is installed.
- After a couple of minutes than we have the generated the GitOps Cluster CRD in the ACM Hub, we will be able to define Applications and ApplicationSets directly from our ACM Hub console in the Applications section.
Deploying ArgoCD/OpenShift GitOps ApplicationSets from ACM Hub
Once we have the integration between OpenShift GitOps and ACM is enabled though the GitOps Cluster CRD in ACM Hub, we have the possibility to deploy ApplicationSets in ACM Hub directly, managing in a single pane of glass all the ArgoCD applications.
On the other hand we will also benefit from the features of the different generators of ArgoCD ApplicationSets.
Using these generators (specially the Cluster Decision Resource Generator) we can deploy several applications from a single repository in different clusters, leveraging from the ApplicationSet for apply the application manifests for the different objects in the repository in each managed cluster.
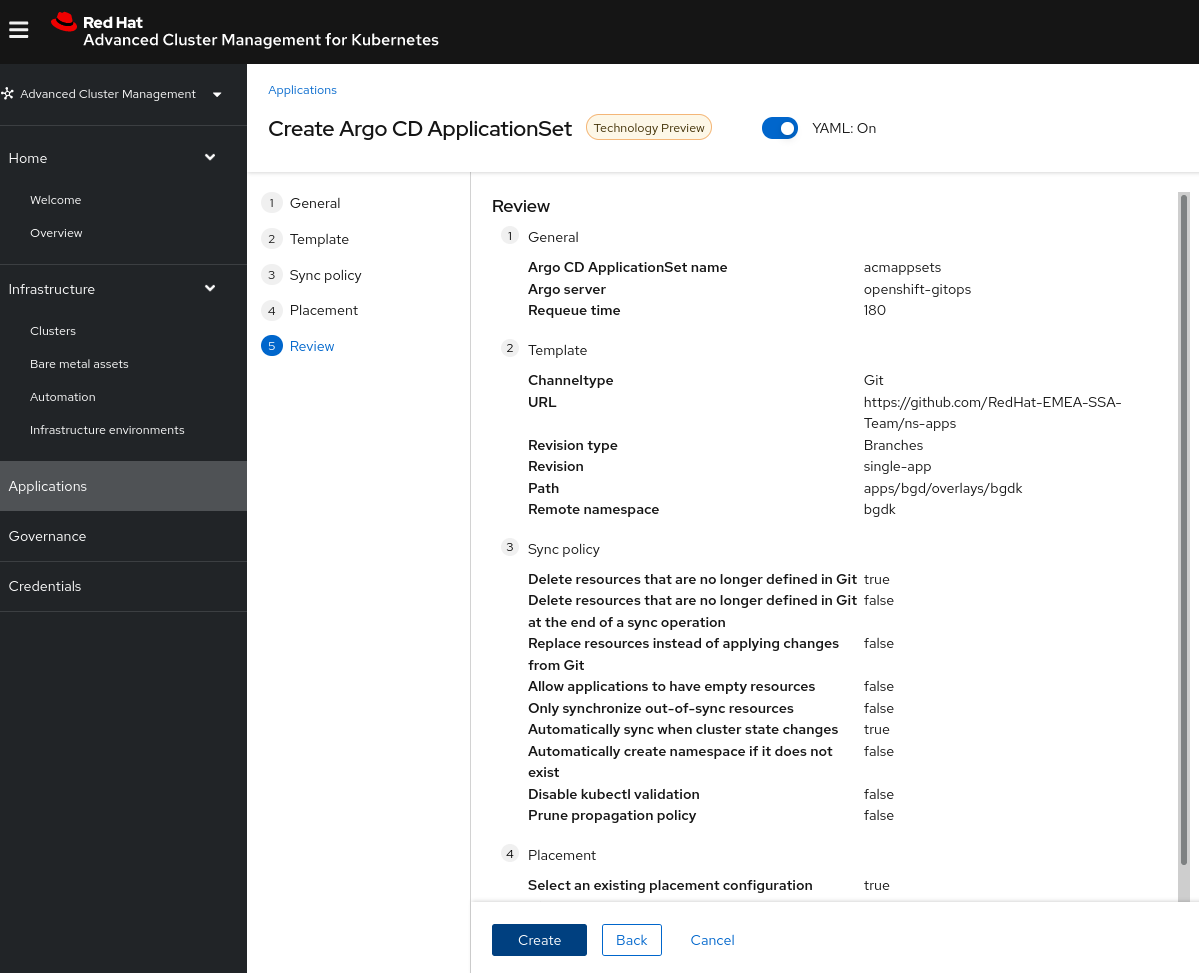
Let’s generate the ApplicationSet in ACM Hub.
- With the UI generate a ApplicationSet with for an applicationset of example:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: ApplicationSet
metadata:
name: acm-appsets
namespace: openshift-gitops
spec:
generators:
- clusterDecisionResource:
configMapRef: acm-placement
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
cluster.open-cluster-management.io/placement: acm-appsets-placement
requeueAfterSeconds: 180
template:
metadata:
name: 'acm-appsets-'
spec:
destination:
namespace: bgdk
server: ''
project: default
source:
path: apps/bgd/overlays/bgdk
repoURL: 'https://github.com/RedHat-EMEA-SSA-Team/ns-apps/'
targetRevision: single-app
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
NOTE: the destination namespace could be openshift-gitops. BGDK could be change, but it leaves in that way because we need to put a destination namespace, even it’s not necessary for the applicationset itself (not needed also for the application bgdk)
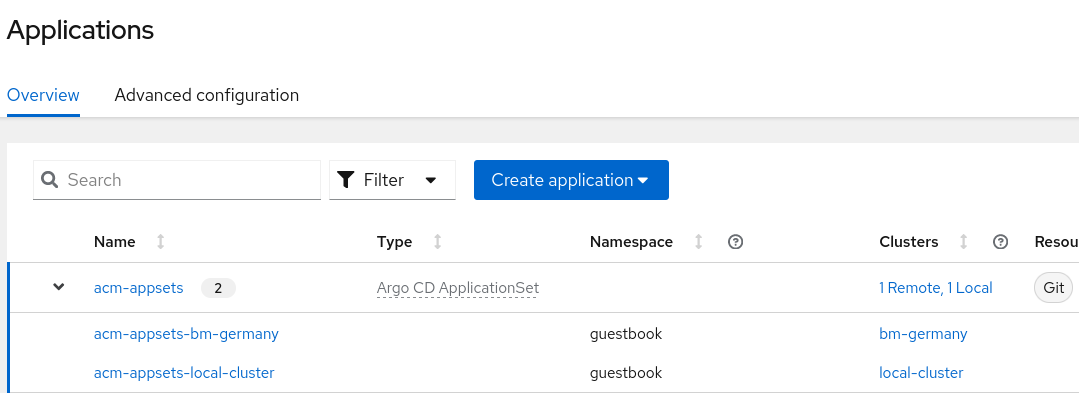
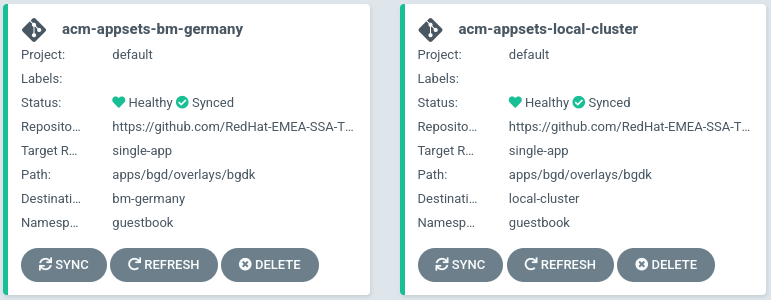
- The result is an ApplicationSet that is generated in OpenShift GitOps but managed by ACM Hub:
as we can see is assigned to two different Clusters, bm-germany and local-cluster that will be where the applications will be deployed managed by the ApplicationSet
The application have the ApplicationSet generated for EACH cluster that matches the Placement defined as acm-appsets-placement, during the definition of the ApplicationSet before. Could also match labels of the clusters, to not depend only of Placement object.
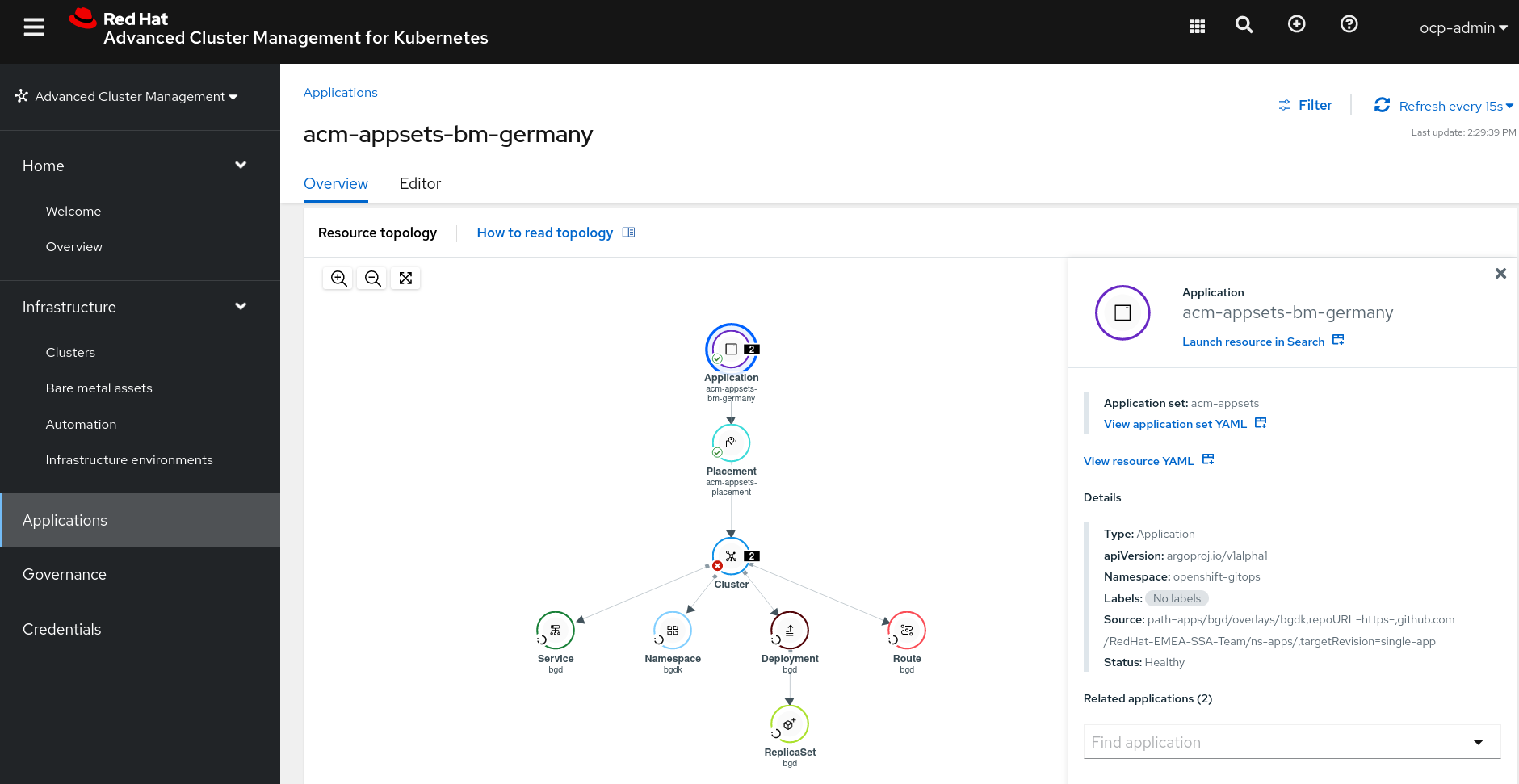
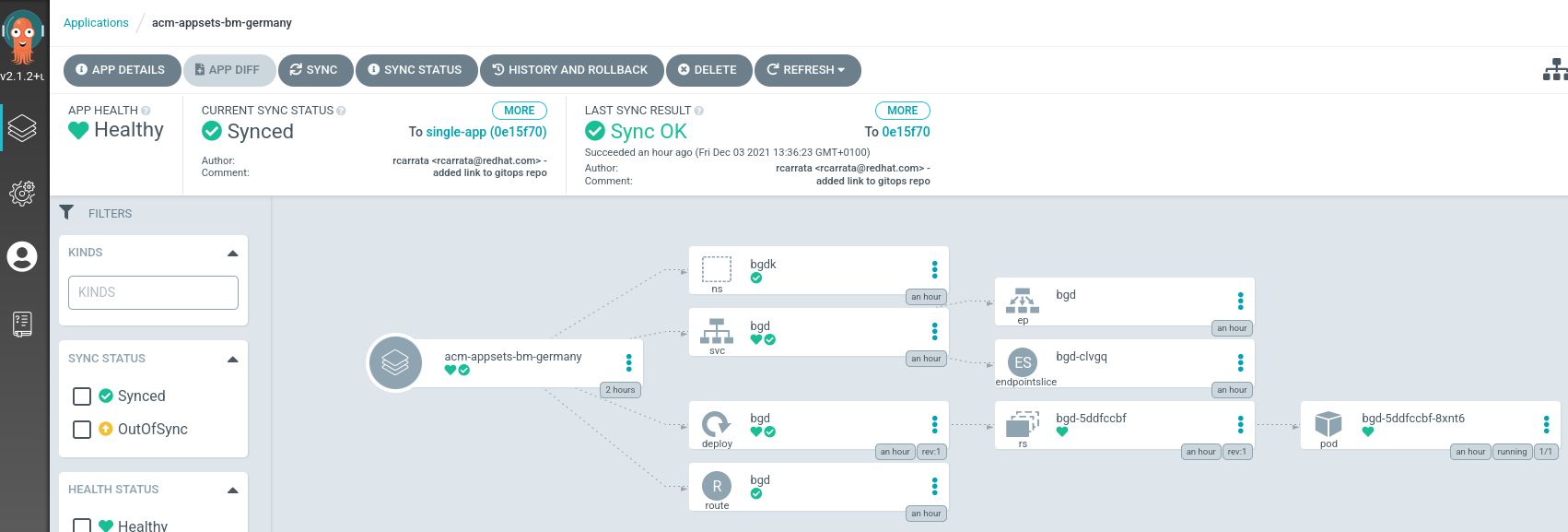
- In the application generated, each of the Application will have their own Application, Placement and Cluster as we can check:
as we can check the ArgoCD Application is deployed correctly and automatically managed by the ApplicationSet of ACM AppSets in the BM-Germany cluster. Also another ArgoCD Application will be used for deploy another Application in the other cluster that matches de Placement.
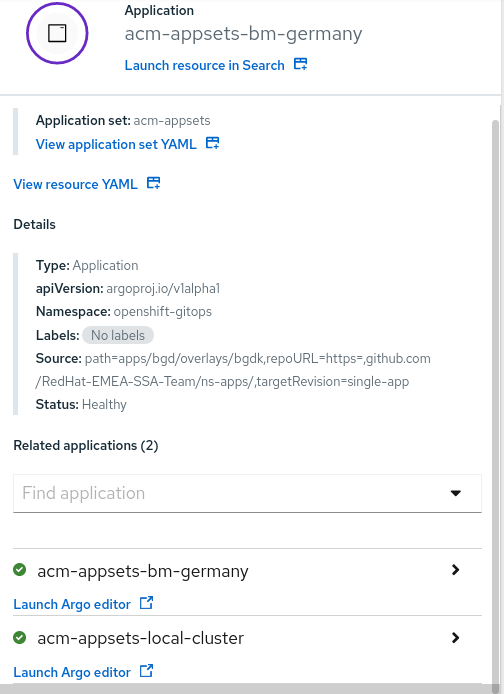
- These are the details of the Application generated by the ApplicationSet:
as we described before two ArgoCD Applications are generated by the ApplicationSet matching the Placement defined.
- In the OpenShift GitOps / ArgoCD argo-controller instance, also two Argo Applications are generated by the ApplicationSet generated by ACM, and each ArgoCD Application is generated for each cluster managed in the ClusterSet that matches with the Placement:
NOTE: check the destination that are pointing to the different managed clusters defined in early steps.
- Each Argo ApplicationSet manages the Application in each cluster managed, like for example the deployment of BGDK application in BM-Germany cluster.
this Application will deploy the application manifests in the managed clusters, deploying in this case the bgdk application manifests (route, service, deployment, etc).
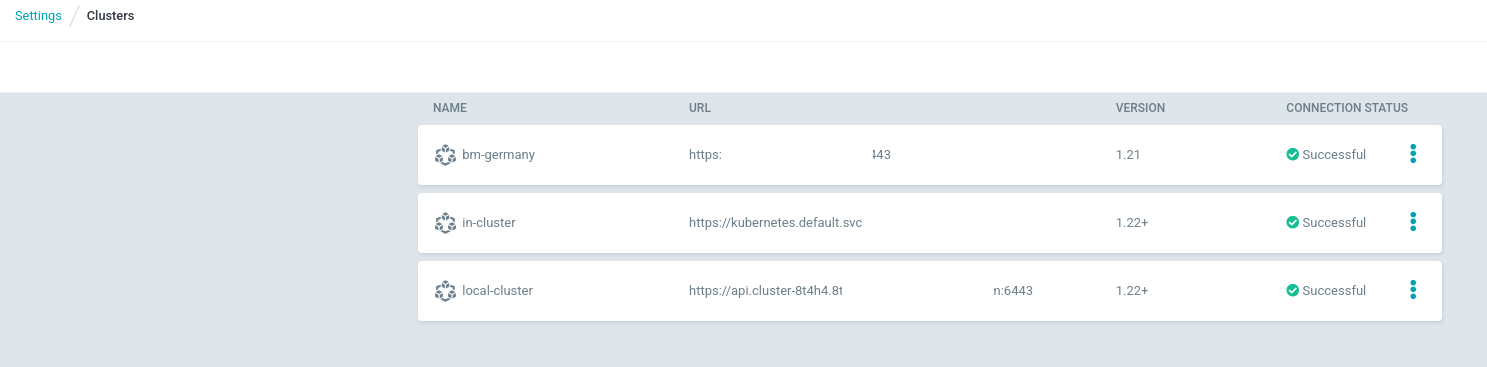
- In the Settings of ArgoCD/OpenShift GitOps, in the Clusters, there are the clusters Managed by ACM with the ClusterSet.
these are generated automatically and managed by the GitOps CRD generated in the ACM Hub, that corresponds with the Managed Clusters.
And with ends this blog post about OpenShift GitOps, ArgoCD ApplicationSets and ACM!
NOTE: Opinions expressed in this blog are my own and do not necessarily reflect that of the company I work for.
Happy multiclustering!